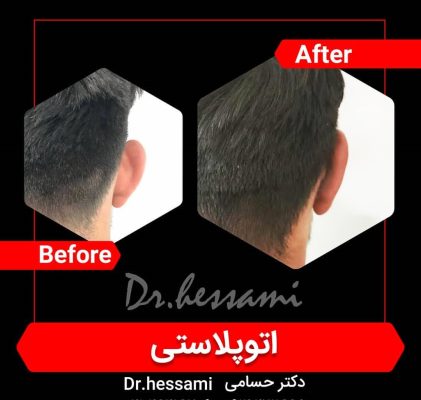
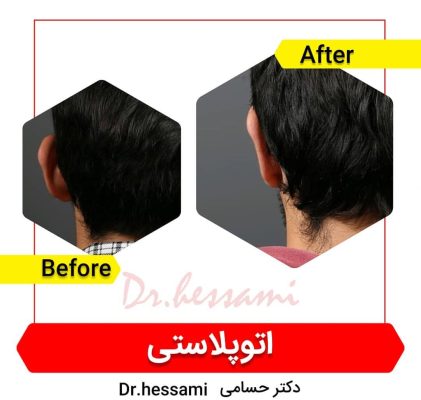
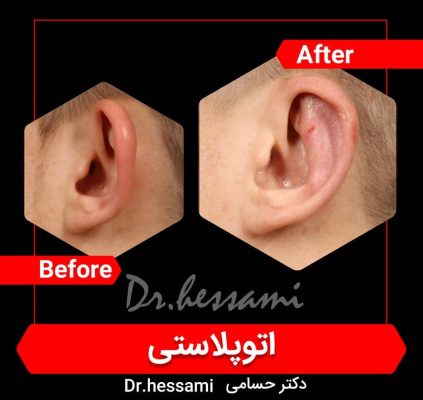
Otoplasty in Iran
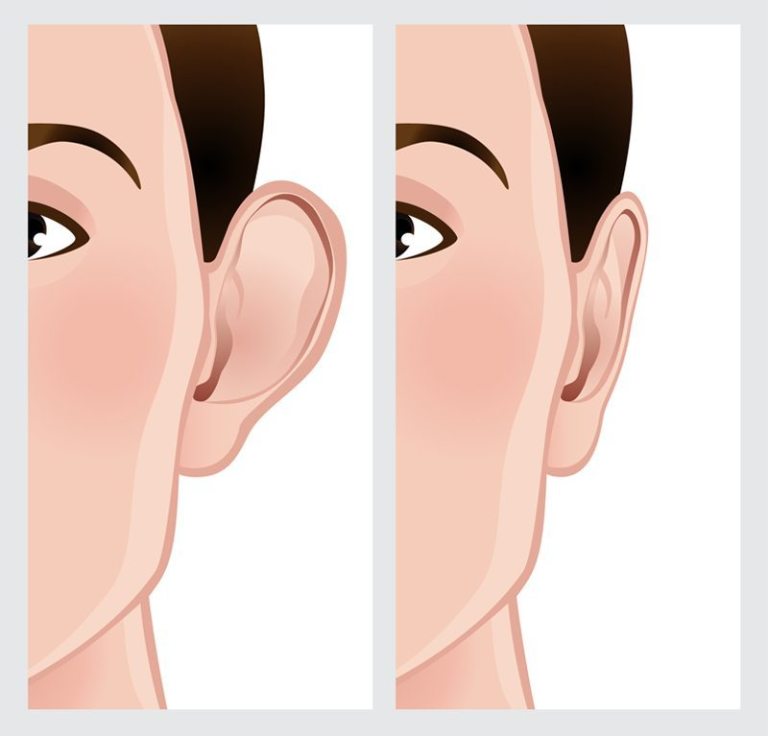
Otoplasty in Iran is a type of cosmetic surgery designed to change the shape, position, or size of the ears. It’s commonly referred to as “ear pinning” when the procedure involves bringing the ears closer to the head. Otoplasty can be performed on children and adults who are self-conscious about their ears and may help with confidence and self-esteem issues.
Reasons for Otoplasty
– Protruding ears: The most common reason for otoplasty is ears that stick out prominently from the side of the head.
– Asymmetrical ears: Some people may have one ear that is positioned differently than the other.
– Abnormal ear shape: This can be due to congenital conditions (like microtia or anotia) or injury.
– Large or stretched earlobes: This can be due to genetics or the result of wearing heavy earrings.
– Previous surgery: Some people may require revision otoplasty if they are not satisfied with the results of an initial ear surgery.
Procedure
– Consultation: A surgeon will discuss the desired results, examine the ears, and explain the procedure.
– Anesthesia: Otoplasty in Iran can be performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the extent of the surgery and patient preference.
– Incision: A small incision is usually made behind the ear to access the cartilage.
– Reshaping: The cartilage is then reshaped, and if necessary, some may be removed to achieve the desired contour.
– Sutures: The ear is then secured in the new position with internal, non-removable sutures. Additional external stitches will close the incision.
Recovery
– Immediate Aftercare: Patients may need to wear a bandage around their head to support the new position of the ears and to protect them.
– Downtime: Most people can return to work or school within a week but should avoid any activity that could bend the ears for at least a month.
– Follow-up: The surgeon will schedule follow-up appointments to monitor the healing process.
– Final Results: Swelling and bruising will gradually subside, and the final results of an otoplasty are usually seen within a few weeks.
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgical procedure, otoplasty in Iran carries some risks, such as infection, adverse reaction to anesthesia, asymmetry, changes in skin sensation, and the need for revision surgery. The skill of the surgeon and the patient’s adherence to pre- and post-operative instructions can help minimize these risks.
Choosing a Surgeon
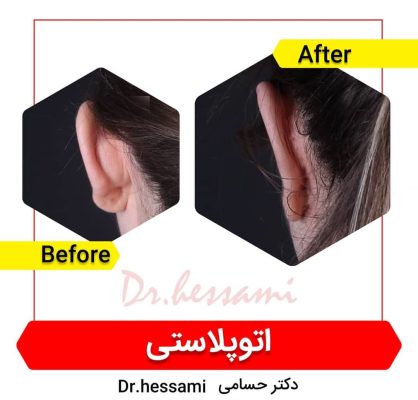
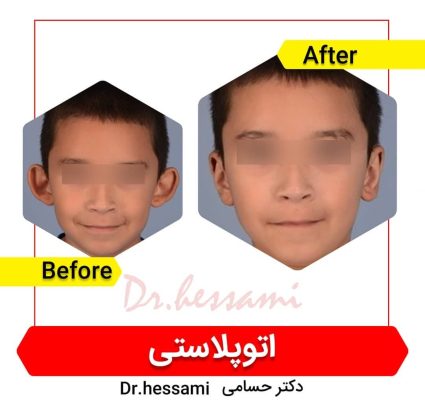
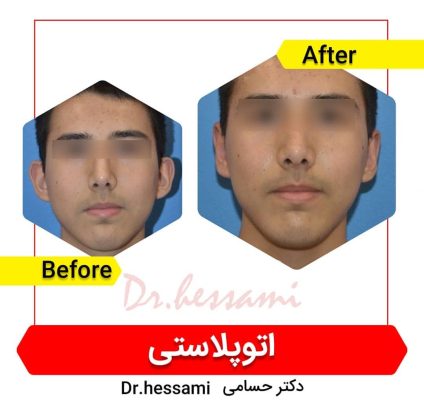
It’s essential to choose a surgeon who is board-certified in plastic surgery and has experience with otoplasty. Reviewing before-and-after photos of previous patients can provide insight into a surgeon’s work and help set realistic expectations.
Before undergoing otoplasty in Iran , individuals should discuss all aspects of the surgery with their healthcare provider to ensure they understand the potential benefits and risks.
Cost and price of otoplasty in Iran
Ear cosmetic surgery in Iran is performed in a hospital
The price of otoplasty in Iran varies between 900 and 1500 euros.
To calculate the price of otoplasty in Iran, send the following advice and information via WhatsApp
- Photo from the front of the face
- Photo from the side of the face
- If you have a specific disease
- how old are you
If you want to operate in Tehran, Dr Hessami, click the button below and follow the stepsStart your therapeutic journey
Types of Otoplasty surgery
Otoplasty in Iran , also known as cosmetic ear surgery, is a procedure to change the shape, position, or size of the ears. It can correct a defect in the ear structure that is present at birth, or it can treat misshapen ears caused by injury. Otoplasty can be performed on children and adults, and there are several types of procedures depending on the correction needed:
1. Ear Pinning
Ear pinning is the most common type of otoplasty. It is typically performed to bring protruding ears closer to the head. This is usually achieved by reshaping the cartilage through incisions behind the ears.
2. Ear Reduction
This type of surgery is designed to reduce the size of large ears. Ear reduction can involve the removal or reshaping of cartilage and skin to create a more proportionate appearance.
3. Ear Augmentation
Some individuals may have underdeveloped ears (microtia) or even completely absent ears (anotia). Ear augmentation is a procedure that aims to construct a normal-looking ear using the patient’s own cartilage, usually taken from the ribs, or using prosthetic materials.
4. Torn Earlobe Repair
Wearing heavy earrings or trauma can lead to torn earlobes. This type of otoplasty involves repairing the split and reconstructing the earlobe.
5. Lop Ear Correction
This procedure corrects “lop ear” deformity, where the tip seems to fold down and forward. Corrective surgery typically involves reshaping the cartilage to create a more natural-looking ear shape.
6. Shell Ear Correction
Shell ear is a condition where certain features of the outer ear, such as the natural folds and creases, are missing. Otoplasty for shell ear involves creating or enhancing these features to give the ear a more normal appearance.
7. Stahl’s Ear Deformity Correction
Also known as “Spock” or “elf ear,” this condition is characterized by an abnormal third fold in the scapha. Surgery to correct Stahl’s ear deformity involves reshaping the cartilage to eliminate the extra fold.
8. Combination Procedures
In some cases, a combination of the above procedures might be performed to achieve the desired outcome, especially when there are multiple issues to be addressed.
Preoperative Considerations
Before undergoing otoplasty, a surgeon will evaluate the condition of the ears and discuss the goals and expectations of the surgery with the patient. It is important to have a clear understanding of what the surgery can and cannot do.
Postoperative Care
After the surgery, patients may need to wear a headband to help maintain the new position and shape of the ears during the healing process. Recovery time and postoperative care will vary depending on the specific procedure performed.
Otoplasty can have a significant positive impact on a person’s self-esteem and quality of life, especially if they have been self-conscious about their ears. As with any surgical procedure, there are risks involved, and it is important to choose a qualified plastic surgeon with experience in ear reconstruction to minimize complications and achieve the best possible result.
Otoplasty incisions
Otoplasty incisions are carefully planned by surgeons to minimize visible scarring. The type and placement of incisions depend on the specific technique used and the individual’s anatomy. Here are the common incision types and their placements for different otoplasty in Iran procedures:
1. Posterior Ear Incision
For the most common type of otoplasty, which is ear pinning, the incision is typically made on the back of the ear. This placement allows the surgeon to access the ear cartilage while keeping the scar hidden behind the ear. The skin is either removed or weakened, and stitches are used to reposition and secure the cartilage closer to the head.
2. Anterior Ear Incision
In some cases, a surgeon may make an incision along the front of the ear, within the folds to conceal the scar. This approach is less common and is usually reserved for more complex cases where additional reshaping is necessary and cannot be accomplished from behind the ear alone.
3. Incision within Natural Creases
Especially in procedures aimed at reducing the size of the ear or creating or enhancing natural folds (such as in shell ear correction), incisions are placed within the natural creases of the ear to hide the scars.
4. Earlobe Incisions
For torn earlobe repair, the incision is made along the tear or the line of the stretched earlobe. After the lobe is repaired, the scar will typically follow the natural contour of the restructured earlobe.
5. Incisions for Ear Augmentation
When constructing a new ear for cases like microtia, multiple incisions may be necessary. These can include incisions where cartilage is harvested (like the ribs), as well as incisions in the region where the ear is being reconstructed. Prosthetic ears also require incisions for placement.
6. Incisions for Stahl’s Ear Correction
To correct Stahl’s ear deformity, the incision is usually made on the back of the ear to access the abnormal cartilage fold. The cartilage is then reshaped or removed to achieve a more typical ear contour.
Postoperative Scarring
After an otoplasty in Iran , scars are usually well-concealed, but they are a normal part of the healing process. Scars may appear red and raised initially but typically fade over time. Proper postoperative care is crucial to minimize scarring, including following the surgeon’s instructions on wound care, avoiding sun exposure, and possibly using silicone sheets or scar creams if recommended.
It’s important for patients to discuss the incision techniques and potential for scarring with their surgeon during the preoperative consultation. A well-trained and experienced plastic surgeon will use techniques that minimize the visibility of scars while achieving the desired cosmetic outcome.
What to expect from Otoplasty surgery
When considering otoplasty surgery, it’s important to have realistic expectations and a good understanding of the procedure, recovery, and potential results. Here’s what to expect at different stages of the process:
Before Surgery
– Consultation: You’ll have a detailed consultation with your plastic surgeon to discuss your concerns and desired outcomes. The surgeon will evaluate your ears, discuss options, and explain the risks and benefits.
– Medical Evaluation: Expect a preoperative medical evaluation to ensure you’re fit for surgery. This may include blood tests or other diagnostic tests.
– Instructions: You’ll receive specific instructions on preparing for surgery, including guidelines on eating, drinking, and which medications or supplements to avoid.
– Photographs: Preoperative photographs are usually taken for medical records and to assist in planning the surgery.
Day of Surgery
– Anesthesia: Otoplasty is commonly performed under local anesthesia with sedation, but general anesthesia may be used, especially for children.
– The Procedure: The surgery typically takes about 2 to 3 hours, depending on the complexity of the procedure.
– Incisions: As previously described, incisions are made in inconspicuous locations to access cartilage for reshaping.
– Closing Incisions: Stitches are used to close the incisions and may be dissolvable or may require removal later.
– Immediate Aftercare: After the procedure, your ears will be covered with bandages to provide support and protect them.
After Surgery
– Recovery Period: You can expect to be in a recovery room for a few hours post-surgery. Most patients can go home the same day.
– Pain and Discomfort: Some pain, swelling, and bruising are normal. Pain can be managed with prescribed or over-the-counter pain relievers.
– Bandages: You’ll wear bandages for several days, and you may need to wear a headband to keep your ears in place for a week or more.
– Follow-Up Appointments: You’ll have appointments to check your healing progress and to remove stitches if they aren’t self-dissolving.
– Activity Restrictions: You’ll be instructed to avoid activities that could bend the ear for a period of time. Most patients can return to work or school within a week, but should avoid strenuous activities for a specified period.
The Results
– Immediate Results: Once the bandages are removed, you’ll notice an immediate change in the position and shape of your ears, although swelling may obscure the final result initially.
– Final Outcome: It can take several weeks for swelling to fully subside. The final shape will be evident once healing is complete.
– Scarring: Scars will mature and fade over time, becoming less noticeable. They are typically hidden in the natural creases of the ear or behind the ear.
Long-Term Expectations
– Permanent Changes: Otoplasty in Iran results are generally permanent, but ears may change shape slightly as part of the natural aging process.
– Satisfaction: Many patients experience a boost in self-confidence and are satisfied with the outcomes.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, there are risks involved such as infection, adverse reactions to anesthesia, bleeding, and dissatisfaction with the cosmetic results. There could also be asymmetry, changes in skin sensation, and in rare cases, damage to the structures of the ear leading to hearing impairment.
It’s important to discuss all of these factors with your plastic surgeon to ensure you have a clear and realistic understanding of what to expect from otoplasty surgery.
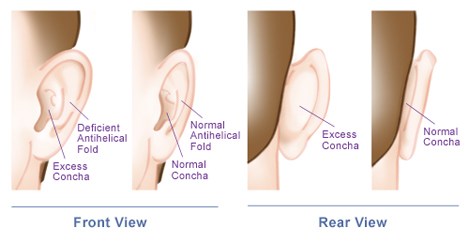
What happens during Otoplasty surgery?
During otoplasty surgery, several steps are followed to achieve the desired correction of the ear’s appearance. Here’s an overview of what typically happens during the procedure:
1. Anesthesia
The first step in otoplasty is administering anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort during the procedure. For adults, local anesthesia with sedation is often sufficient, whereas general anesthesia may be preferred for children or for more complex cases.
2. Making the Incision
Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the surgeon will make incisions behind the ear or within its inner creases. The location and pattern of the incisions depend on the specific goals of the surgery. For instance, incisions for ear pinning are usually made on the back surface to minimize visible scarring.
3. Reshaping the Ear Structure
The next step involves reshaping the ear cartilage to achieve the desired appearance. This can include:
– Trimming or Removing Cartilage: In cases where the ear size is being reduced, the surgeon may trim or remove excess cartilage and skin.
– Folding or Shaping Cartilage: For protruding ears, the cartilage may be folded and secured with internal stitches to pull the ear closer to the head.
– Grafting: In cases of ear augmentation, cartilage (often from the ribs) may be grafted to create a more natural ear shape.
4. Internal Stitches
Permanent or dissolvable stitches are used to hold the newly shaped cartilage in place. The internal sutures are key to creating the new ear contour.
5. Closing the Incisions
The surgeon will close the incisions with stitches that may need to be removed later, or they may use dissolvable sutures that will be absorbed by the body over time.
6. Checking for Symmetry
During the surgery, the surgeon will frequently check the ears for symmetry and make adjustments as necessary to ensure that both ears are as symmetric as possible.
7. Bandaging
After the surgery is completed, the ears are wrapped in soft dressings to protect them and to aid in the initial phase of healing. These bandages also help maintain the new shape of the ear.
8. Recovery
Following the procedure, the patient is taken to a recovery area where they are monitored as the anesthesia wears off. Patients are typically discharged the same day, though they will need someone to drive them home.
During the recovery period, it is crucial to follow the surgeon’s aftercare instructions to ensure proper healing and the best possible outcome. This includes wearing any additional support garments, attending follow-up appointments, and adhering to activity restrictions.
That’s the general process for a typical otoplasty in Iran . However, the specifics can vary depending on the individual’s needs and the surgeon’s techniques. It’s important to have a thorough consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon to understand exactly what your procedure will entail.
How is the recovery process after a otoplasty in Iran?
Recovery from otoplasty in Iran is a critical phase where proper care and following your surgeon’s instructions are essential for achieving the best results and minimizing the risk of complications. Here’s what you can generally expect during the otoplasty in Iran recovery process:
Immediate Postoperative Period
– Bandages: Your ears will be covered with bandages immediately after surgery to protect them and aid in the initial healing process.
– Discomfort: You may experience some discomfort and pain, which can be managed with prescription or over-the-counter pain medication as recommended by your surgeon.
– Rest: It’s important to rest with your head elevated to reduce swelling.
– Care Instructions: You’ll be given specific instructions on how to care for your surgical site, medications to take to aid healing and reduce the risk of infection, and when to follow up with your surgeon.
The First Week
– Bandage Removal: The heavy bandages are often removed after a few days and may be replaced with lighter dressings or a headband.
– Swelling and Bruising: Expect some swelling and bruising, which will peak within the first week and then gradually subside.
– Activity Restrictions: You should avoid any activities that might put pressure on your ears, like sleeping on your side, wearing glasses, or any strenuous activities.
Following Weeks
– Return to Normal Activities: Many patients can return to work or school within about a week, but you should still avoid any vigorous activities that could impact the ears.
– Visible Improvements: As the swelling decreases, the improvements in the ear’s appearance will become more apparent.
– Wearing a Headband: You may be advised to wear a headband to keep your ears in the correct position, particularly at night, for a few weeks after the initial bandages are removed.
Long-Term Recovery
– Final Results: It can take up to six weeks for most of the swelling to resolve, but subtle changes and maturation of scars can continue for up to a year.
– Scars: Incision lines will continue to refine and fade for up to a year. They are usually well-concealed in the natural creases of the ear or behind the ear.
– Follow-Up Visits: Ongoing follow-up visits will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Tips for a Smooth Recovery
– Follow All Instructions: Adhere strictly to your surgeon’s postoperative instructions.
– Keep Your Head Elevated: To minimize swelling, keep your head elevated, especially when sleeping, for the first few days.
– Avoid Pressure: Do not put any unnecessary pressure on your ears; be careful when putting on and taking off clothing.
– Stay Hydrated and Eat Healthily: Good nutrition and hydration are vital for healing.
– Avoid Sun Exposure: Protect your ears from the sun to prevent worsening of scars and prolonged swelling.
– Avoid Smoking: Smoking can impede the healing process and should be avoided.
Complications to Watch For
Contact your surgeon if you experience any signs of complications, such as increased pain, warmth, redness, discharge from the incision sites, fever, or any other symptoms that seem abnormal.
Remember that everyone heals at a different rate, and your recovery may not match another person’s experience exactly. Always follow the personalized advice provided by your plastic surgeon for the best results.
Diet after otoplasty in Iran
After otoplasty in Iran , there isn’t a specific diet that you must follow, but a balanced, healthy diet can help promote healing and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some general dietary guidelines you might consider following during your recovery:
Stay Hydrated
– Water: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, which is essential for the healing process.
– Avoid Alcohol: You should avoid alcohol, especially if you’re taking prescription pain medication, as it can increase the risk of bleeding and swelling.
Nutrient-Rich Foods
– Protein: Consuming enough protein is vital for tissue repair. Include lean meats, beans, tofu, or dairy products in your diet.
– Vitamins and Minerals: Fruits and vegetables high in vitamins C and A can help with healing. Vitamin C is important for collagen production, and vitamin A supports the immune system and skin health.
– Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help reduce inflammation.
Gentle Eating
– Easy-to-Eat Foods: Initially, you may want to eat foods that don’t require a lot of chewing, as the act of chewing can create movement in the facial muscles and around the ears.
– Avoid Excessive Salt: Eating foods high in salt can increase swelling, so it’s best to limit your sodium intake during recovery.
Avoid Certain Supplements and Foods
– Blood-Thinning Agents: Some foods and supplements have blood-thinning effects, such as vitamin E, garlic, ginkgo biloba, and fish oil. It’s best to discuss with your surgeon which supplements or foods you should avoid before and after surgery to prevent excessive bleeding.
Small, Frequent Meals
– Frequent Meals: If you’re experiencing nausea, which can sometimes occur after anesthesia, small and frequent meals may be more manageable.
Fiber-Rich Foods
– Constipation Prevention: Pain medications can cause constipation, so including fiber-rich foods in your diet like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can help maintain bowel regularity.
Special Considerations
If you have specific dietary restrictions or health conditions that require a special diet, discuss these with your surgeon prior to surgery. They may refer you to a nutritionist to help plan your meals during the recovery phase.
Remember, the primary goal is to support your body’s healing process, so a balanced diet that is rich in essential nutrients will contribute to a smoother recovery. Always follow your surgeon’s and healthcare team’s recommendations regarding diet, medication, and overall postoperative care.
How do you sleep after a Otoplasty?
After otoplasty in Iran , how you sleep is important for both your comfort and the proper healing of your ears. Here are some tips to help you sleep better and protect your ears while they heal:
1. Keep Your Head Elevated
– Sleep with your head elevated on pillows to reduce swelling and discomfort. This position can also reduce the risk of accidentally rolling onto your side and putting pressure on your ears.
2. Use a Travel Pillow
– A travel neck pillow can help keep your head from turning side-to-side and may offer some protection if you do roll over.
3. Back Sleeping
– Try to sleep on your back exclusively. This is the safest position to avoid putting any pressure on your ears. If you’re not used to back sleeping, practice sleeping on your back in the days leading up to the surgery.
4. Avoid Pressure on the Ears
– Do not sleep on your side, especially on the operated ear, as this can cause pain and may disrupt the healing process.
5. Prepare Your Sleeping Area
– Arrange your sleeping area so everything you need is within easy reach. This will help you avoid having to turn your head excessively during the night.
6. Pain Management Before Bed
– Take any prescribed pain medication according to your surgeon’s instructions; managing pain before bed should help you sleep more comfortably.
7. Relaxation Techniques
– Use relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or listening to calming music to help you fall asleep more easily.
8. Follow Your Surgeon’s Advice
– Your surgeon may provide you with a postoperative headband to wear to support your ears, especially during sleep. Wear it as directed to ensure your ears are protected.
9. Avoid Strenuous Activities Before Bed
– Avoiding strenuous activities before bedtime can help your body stay in a more relaxed state and promote better sleep.
10. Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule
– Go to bed and wake up at the same times each day to help regulate your sleep cycle.
11. Keep Your Sleeping Area Quiet and Dark
– Minimize disruptions by keeping your sleeping area quiet and dark. Use earplugs if ambient noise is an issue, provided they do not put pressure on your ears.
12. Stay Hydrated, But Not Right Before Bed
– While it’s important to stay hydrated for healing, try to avoid drinking large amounts of liquids right before bedtime to reduce the need for nighttime trips to the bathroom.
Remember, proper rest is crucial for your recovery. If you’re having trouble sleeping after your otoplasty, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for advice. They may have additional recommendations or adjustments to make your recovery process as comfortable as possible.
The best age to have a Otoplasty
Otoplasty in Iran , also known as ear pinning surgery, can be performed at almost any age after the ears have reached near full size, typically around age 5 to 6. There are several considerations when determining the best age for otoplasty:
For Children
– Ear Development: By age 5 or 6, a child’s ears have usually reached about 85% of their adult size, making this an ideal time for surgery from an anatomical standpoint.
– Psychological Benefits: Having the surgery before starting school can help avoid potential psychological distress from teasing or bullying related to protruding ears.
– Resilience: Children often have a quicker healing time and may be less aware of the discomfort associated with surgery and recovery compared to adults.
For Adults
– Stable Expectations: Adults can make fully informed decisions about the surgery and have stable expectations regarding the outcome.
– Health Considerations: Adults need to be in good overall health to minimize the risks associated with surgery. Certain medical conditions may impact the timing and advisability of cosmetic surgery.
– Lifestyle Considerations: Adults may need to consider time off work and their ability to follow post-operative care instructions when planning their surgery.
General Considerations
Regardless of age, the candidate for otoplasty should be in good general health, not have any life-threatening illnesses or untreated chronic ear infections, and have realistic expectations about the results. It’s also important for the patient or, in the case of children, the parents to understand the risks and the recovery process associated with the surgery.
Psychological and Social Factors
The psychological and social factors are particularly significant when considering otoplasty for children. While some parents opt to have their child undergo otoplasty at a young age to avoid potential emotional distress, others may prefer to wait until the child is old enough to participate in the decision.
Consultation with a Specialist
Before proceeding with otoplasty in Iran , a thorough consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon or a facial plastic surgeon is essential to discuss the potential benefits and risks, as well as to set realistic expectations. The surgeon can also assess the specific anatomical considerations of the patient’s ears and recommend the best timing for the procedure.
In summary, while early childhood is often considered the best time for otoplasty from a developmental standpoint, the decision should be individualized based on the physical and emotional readiness of the child, as well as the preferences and informed consent of the family. Adults can undergo otoplasty at any age, provided they are good candidates for surgery.
How long can you exercise after a Otoplasty?
After undergoing otoplasty in Iran , it’s important to allow your body time to heal before resuming exercise or vigorous activities. The timeline for returning to exercise can vary depending on the extent of the surgery, the individual’s healing process, and the surgeon’s instructions. However, here is a general guideline for resuming exercise after otoplasty:
Initial Recovery Period (First Week)
– First 24 to 48 Hours: Rest is crucial; avoid any form of exercise or strenuous activity.
– First Week: Light walking is typically allowed to promote circulation, but it’s important to avoid any activity that could lead to an increased heart rate or blood pressure, which can cause bleeding or more swelling.
Gradual Resumption of Activities (2 to 4 Weeks)
– After the First Week: Light activities can often be resumed, but still avoid any activity that significantly increases blood pressure or risks impact to the ears.
– 2 to 3 Weeks: Moderate exercise such as light jogging or stationary cycling might be permitted, but contact sports or exercises that could jar or impact the ears should continue to be avoided.
Full Exercise (4 to 6 Weeks and Beyond)
– 4 to 6 Weeks: Most patients are cleared to resume all types of exercise, including lifting weights and high-impact aerobic activities, as long as the healing process is progressing well.
– 6 Weeks and Beyond: Contact sports or activities with a high risk of an ear injury should be avoided until the surgeon gives a clear go-ahead, which may be around 6 to 8 weeks post-surgery, or even longer in some cases.
Important Considerations
– Follow Your Surgeon’s Advice: Always follow the personalized advice and instructions from your surgeon, as they know the details of your surgery and how you are healing.
– Listen to Your Body: If you experience pain, discomfort, or any new swelling while exercising, stop immediately and consult your surgeon.
– Protect Your Ears: When you do resume exercise, take care to protect your ears from any potential trauma. This may involve wearing a headband or avoiding certain exercises or sports where the ears could be bumped or injured.
Your surgeon will typically schedule follow-up appointments to check on your recovery and will advise you when you can increase your activity level. It’s essential to attend these appointments and get clearance from your surgeon before returning to your regular exercise routine.
Otoplasty surgery is not suitable for whom
Otoplasty in Iran , like any surgical procedure, is not suitable for everyone. Certain conditions or circumstances may make otoplasty less advisable or even contraindicated for some individuals. Here are some general considerations that might indicate otoplasty is not suitable:
Medical Conditions
– Chronic Ear Infections: Active or chronic ear infections need to be resolved before considering otoplasty.
– Bleeding Disorders: Conditions that affect blood clotting can increase the risk of complications during and after surgery.
– Cardiovascular Diseases: Individuals with serious heart conditions may face increased risks from surgery and anesthesia.
– Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can impair healing and increase the risk of infection.
– Immune System Disorders: Conditions that weaken the immune system can also slow healing and raise the risk of infection.
– Poor Overall Health: Patients who are in poor health or who have multiple medical conditions that impact their ability to heal may not be suitable candidates.
Psychological Readiness
– Realistic Expectations: Patients must have realistic expectations about what otoplasty can achieve. Those seeking perfection or expecting the surgery to dramatically change their life or self-esteem might be disappointed.
– Mental Health Issues: Those with untreated or unstable mental health issues may not be suitable candidates until their condition is well-managed, as they may have difficulty coping with the stress of surgery and recovery.
Lifestyle Factors
– Smoking: Smoking can significantly impair healing and increase the risk of complications. Surgeons typically require patients to quit smoking well in advance of the procedure and throughout the recovery period.
– Alcohol Use: Excessive alcohol consumption can also impair healing and increase surgical risks.
– Non-compliance with Aftercare: Patients who are unlikely to follow postoperative instructions, including activity restrictions, medication regimens, and follow-up appointments, may not be good candidates for surgery.
Age Considerations
– Young Children: Although otoplasty can be performed on children, very young children (under 5 years) are typically not suitable candidates because their ears are still growing and developing.
– Elderly Patients: While there is no absolute age limit for otoplasty, older adults may have increased surgical risks and slower healing times, which need to be carefully evaluated.
Cosmetic Expectations
– Minor Irregularities: Those seeking to correct very minor imperfections may not be suitable candidates if the risks of surgery outweigh the benefits.
– Previous Surgeries: Individuals who have had multiple ear surgeries may have scar tissue that could complicate otoplasty in Iran and impact the aesthetic outcome.
It’s important to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to determine whether otoplasty in Iran is a good option. The surgeon will perform a thorough evaluation, which includes a medical history, physical exam, and discussion of the potential risks and benefits, to ensure that the patient is a suitable candidate for the procedure.